Membranous nephropathy
• MN เป็น most common cause NS ใน caucasian adultพบ subepithelial immune deposit ทำให้ glomerular capillary wall ผิดปกติ à GBM spike
• แบ่งเป็น primary and secondary
• Primary MN เป็น prototype ของ in situ complex formation
• Secondary MN จาก autoimmune, malignancy, infection, expose therapeutic agents
ลักษณะสำคัญของ MN
1. Proteinuria : nephrotic range ประมาณ 50% มี microscopic hematuria
2. Renal function ยังดีอยู่
3. ใน primary พบใน adult, secondary พบในเด็กและคนแก่กว่า 60 ปี
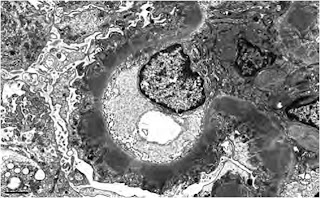
Pathology
LM: normocellular, patent capillary lumen พบ GBM thickeningจากการที่มี subepithelial immune deposit ถ้าย้อม silver และ PAS จะเห็น GBM spike ชัดขึ้น ถ้าย้อม trichrome อาจเห็น fuchsinophillic immune deposit เป็นสีส้มแดง ต้องมองหา fibrin thrombi เนื่องจากมักพบร่วมกับภาวะ hypercoagulable state, renal vein thrombosis
· ใน MN มักไม่พบ crescent ถ้าพบต้องตรวจ anti GBM antibody, ANCA, SLE
อาจพบมี tubulointerstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy ร่วมด้วยตาม severity เป็นตัวช่วยบอก prognosis ของผู้ป่วย MN
IF: subepithelial deposit ส่วนใหญ่เป็น IgG, Kappa, Lambda ติด c3 น้อยกว่า ส่วน IgM,IgA, C1q พบน้อย
EM: เป็นการเปลี่ยนแปลงของ GBM แบ่งเป็น 4 stage Ehrenreich &Churg staging
1. Small and sparse subepithelial deposits ทำให้ GBM ดูหนาขึ้นหรือเป็นปกติ อาจเห็นเพียง loop ดูแข็งๆตึงๆ podocyte swelling ยังไม่เห็น spike
2. เป็น stage ที่มักพบได้บ่อย เห็นsubepithelial deposit มี projection ของ GBM เห็นเป็น spike
3. Subepithelial deposits และ GBM spike ถูกปกคลุมด้วยoverlying neomembrane formation ทำให้ดูหนาต่อเนื่องกันไป
4. Deposit กลายเป็น electron lucent เนื่องจากเกิด resorption
Ehrenreich &Churg staging ช่วยให้เข้าใจ process ของ subepithelial deposit formation แต่ไม่ช่วยเรื่อง clinical correlation ทั้งปริมาณ Proteinuria, renal function, prognosis
ลักษณะทาง patho ที่ช่วย predict renal survival ไม่ดีได้แก่
- Degree of tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis
- Development ของ segmental glomerulosclerosis
- Intensity ของ complement deposition จาก IF
- Heterogenous deposit เจอว่ามี deposit หลาย stage
Secondary forms ของ MN พบประมาณ 25% แบ่งเป็น4 กลุ่ม
- Autoimmune : SLE (MC), RA, Sjogren, MCTD, sarcoidosis, grave’s, hashimoto
- Malignancy : lung, prostate, breast, GI tract พบบ่อยในคนอายุเกิน 60 ปี มีประวัติสูบบุหรี่
- Drugs : gold, penicillamine, NSAIDS, cox2 inh, captopril
- Infections : HBV, HCV, syphilis, parasites
Primary MN มักพบ isolated subepithelial immune deposits ติด IgG predominate
Secondary MN
- Mesangial or endocapillary proliferation
- Deposit at other site เช่น mesangial , subendothelial, tubular BM
- Full house staining IgG, IgM, IgA and C3, C1q
- Ultrastructural finding of endothelial tubuloreticular inclusion
- ยกเว้น neoplasia associated MN มักแยกไม่ได้จาก primary MN
- การใช้ subclass IgG แยก โดย
o Primary MN : เด่น IgG4 , ติด IgG1 บ้างเล็กน้อย
o MN Lupus nephritis: ติดทุก subclass ของ IgG แต่ IgG4จะเด่นน้อยกว่า
o Malignancy related : ติด IgG1,2,4 แต่ไม่ติด IgG3
Pathogenesis
Heymann nephritis model : rat model à ฉีด antibody ต่อ fractionated renal cortex enriched in proximal brush border (Fx1A) ซึ่งมี immunogenic component ที่สำคัญคือ Gp 330/megalin อยู่ที่ prox tubular brush border and podocyte foot process ในหนู ทำให้หนูเป็น MN เนื่องจาก กระตุ้นให้ podocyte หลั่งสาร protease, TGF B, oxidant ลักษณะที่สำคัญของ in situ immune complex
Human Heymann nephritis antigenà พบครั้งแรกในเด็กแรกเกิด ชื่อ Neutral endopeptidase (NEP) ทำให้เด็กเป็น congenital MN ล่าสุดที่พบคือ M-type antiphospholipase receptor (PLA2R) เป็นสาเหตุให้เกิด primary MN ในคน ใช้ตรวจวินิจฉัยและเป็น marker สำหรับดูresponse การรักษาได้ และเมื่อไม่นานมานี้พบว่า MN เกี่ยวข้องกับ HLA-DQA1 allele chromosome 6p21
Pathogenesis ของ secondary MN เกิดจาก antibody ต่อ nonglomerular antigen แล้วไปติดอยู่ที่ subepithelial ของ GBM เนื่องจากมีขนาดเล็กและมีความเป็น cationic charge แล้วไปจับกับ in situ circulating antibody เกิดเป็น MN
 |
| ปลาทู อิอิ ^_^ |




ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น